Abstract
While Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and the Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV)/human herpesvirus (HHV) 8 have shown a definite association with lymphoproliferative disease, a role for the HHV-6 has been less clear. Similar to other herpesviruses, HHV-6 predominantly remains latent following initial infection, but can be reactivated during stress or immune suppression, and is the cause of roseola in young children. Existing as two distinct species, HHV-6B is more common, infecting ~90% of adults.
HHV-6B, a T-lymphotropic virus, enters cells via CD134, a TNF receptor superfamily member, expressed on both naïve and CD4 +CD25 + T cells, leading to CD4 + lymphocyte depletion and impaired T cell activation. HHV-6 has been variably detected in classic Hodgkin (CHL) and T-cell lymphomas (TCL) by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and PCR with more recent data suggesting infection may be confined to tumor-associated lymphocytes. The specificity of these IHC antibodies is not well documented. The question remains whether HHV-6 in the tumor microenvironment of advanced disease is a consequence of immune dysfunction, or may play a more direct role in tumor initiation and progression by altering the tumor microenvironment. To address these questions, we evaluated HHV-6B viral gene expression patterns in lymphoma patient samples by RNA sequencing techniques.
Following IRB approval, CHL, TCL, B-cell, and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) cases were screened for potential HHV-6-association by IHC with an antibody against HHV-6 gp60/110 envelope glycoprotein (Millipore Sigma, MAB8537). Positive cases with available frozen tissue and adequate RNA (5) or sorted T-cell subsets from Hodgkin lymphoma (11) underwent bulk RNA-seq (rRNA depletion (Illumina), 50M reads/sample). Viral transcripts were identified by performing the Burrows-Wheeler Alignment by reference host alignment (to filter host and bad quality reads) followed by viral reference host alignment. Previous TCL databases with available RNAseq data were similarly evaluated.
IHC analysis revealed 5/25 CHL, 34/52 TCL, 5/13 PTLD, 4/81 diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 2/28 follicular lymphoma (FL) with rare gp60/110-positive cells. This included 11 CHL cases with sorted T-cell subsets, of which one showed membranous and Golgi gp60/110 staining in background T-cells (25-year-old female, nodular sclerosis subtype, EBV-negative). Of these 11 CHL cases, RNAseq of T-cell subsets revealed a pattern of HHV-6B transcripts in only this case. Frozen tumor blocks were available from 5 additional cases with positive gp60/110 staining (2 CHL, 1 DLBCL, 1 FL and 1 PTLD), but RNAseq analysis did not identify any HHV-6B transcripts. Notably, these cases had dim cytoplasmic but not Golgi gp60/110 staining.
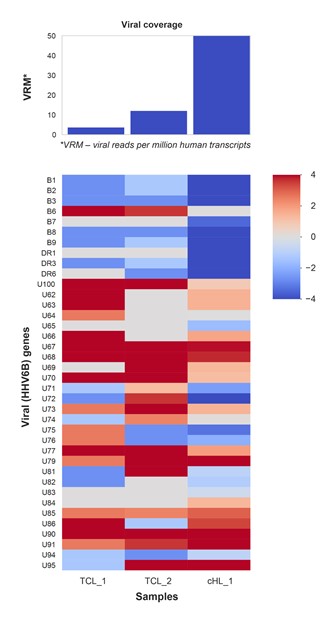
RNA sequencing data derived from two independent TCL cohorts were analyzed for HHV-6B transcripts. Although no HHV-6B transcripts were detected via RNAseq in 20 angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma samples from one TCL cohort, many had EBV-gene expression. HHV-6B transcripts were detected in two cases of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) in a second TCL cohort (2/79 cases). High expression of the U67, U68, U79 and U90 genes was found, revealing overlap of the HHV-6B transcript expression between ALCL and CHL samples (Fig 1). Additionally, detection of two genes that could be driving tumor growth (U51, which encodes a G-protein receptor and U24, which inhibits proper T cell activation, reducing secretion of cytokines at infection site) demonstrates a specific viral gene expression pattern within the intratumor T-cell population.
The potential presence of HHV-6B infection in the lymphoma microenvironment is controversial. To our knowledge, this is the first report conclusively demonstrating HHV-6B expression in CHL using RNAseq. Notably, the viral gene expression pattern seen in CHL overlaps with that found in two cases of ALCL, highlighting viral proteins of potential particular significance. These data may aid in development of a more reliable means of HHV-6B detection. For example, the immediate early gene U90, a transcriptional activator that may induce expression of both viral and cellular genes that affect the tumor microenvironment, was consistently expressed and may be a reliable marker of HHV-6B infection.
Funding: HHV-6 Foundation
Tychinin: BostonGene Inc.: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Patents & Royalties. Karelin: BostonGene Inc.: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Patents & Royalties. Cherdintsev: BostonGene Inc.: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Patents & Royalties. Kudryashova: BostonGene: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Patents & Royalties: BostonGene. Egorov: BostonGene: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Patents & Royalties. Degryse: BostonGene Inc.: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Kotlov: BostonGene Corp: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Patents & Royalties. Bagaev: BostonGene Corp.: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Patents & Royalties: BostonGene. Roth: Merck: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy. Roshal: Celgene: Other: Provision of services; Physicians' Education Resource: Other: Provision of services; Auron Therapeutics: Other: Ownership / Equity interests; Provision of services. Rabadan: Genotwin: Other: Raul Rabadan is founder of Genotwin; AimedBio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Elemento: Owkin: Consultancy, Other: Current equity holder; Freenome: Consultancy, Other: Current equity holder in a privately-held company; Volastra Therapeutics: Consultancy, Other: Current equity holder, Research Funding; One Three Biotech: Consultancy, Other: Current equity holder; Janssen: Research Funding; Eli Lilly: Research Funding; Champions Oncology: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Johnson and Johnson: Research Funding.